The ORNL DAAC recently released a new Arctic-Boreal Vulnerability Experiment (ABoVE) dataset by Zhang, Y., et al. (2021):
ABoVE: Landsat-derived Annual Disturbance Agents Across ABoVE Core Domain, 1987-2012
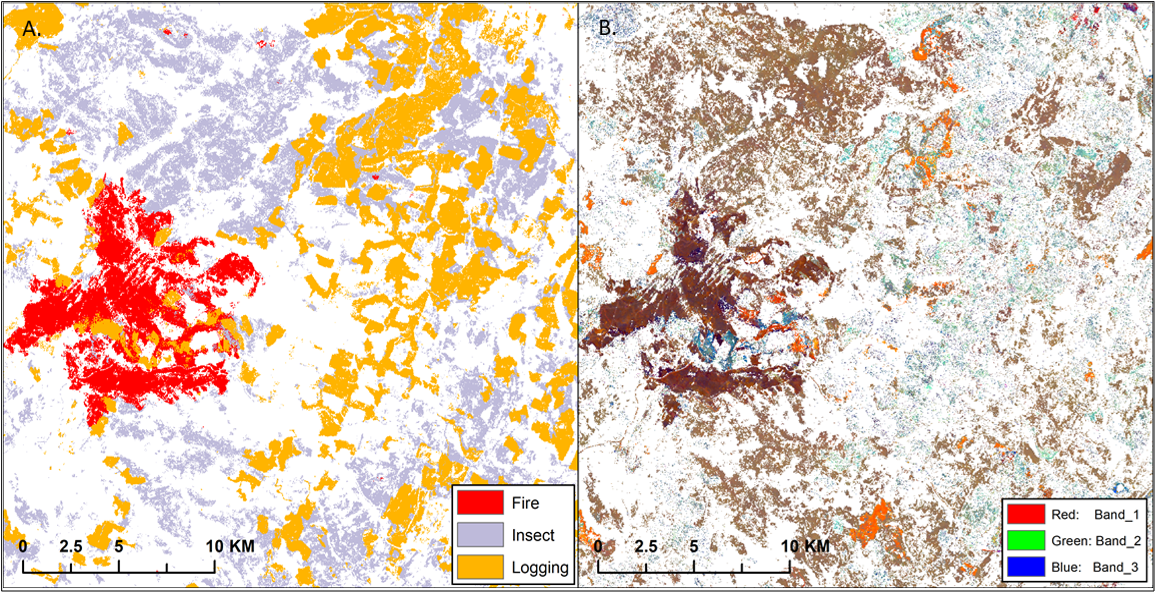
This dataset provides spatial data on disturbance agents of fire, insects, and logging in the Arctic Boreal Vulnerability Experiment (ABoVE) core domain at an annual time step from 1987-2012 and 30 m resolution. Using a time-series of Landsat data, the three disturbance types were identified by abrupt changes in Tasseled Cap (dTC) indices of brightness, greenness, and wetness. Disturbances were detected by a Continuous Change Detection and Classification (CCDC) harmonic regression model applied to the time series. The dTC indices and disturbance results are provided.
The mapped disturbance agents were derived from Thematic Mapper (TM) and Enhanced Thematic Mapper (ETM+) observations across 164 ABoVE tiles. The product uses the Land Cover product for differentiating disturbances to forest or non-forest land covers (Wang et al., 2019a). The dTC images for deriving causal agents of disturbance are provided at an annual step from 1985–2012.
The ABoVE is a NASA Terrestrial Ecology Program field campaign being conducted in Alaska and western Canada, for 8 to 10 years, starting in 2015. Research for ABoVE links field-based, process-level studies with geospatial data products derived from airborne and satellite sensors, providing a foundation for improving the analysis, and modeling capabilities needed to understand and predict ecosystem responses to, and societal implications of, climate change in the Arctic and Boreal regions.
Additional data from ABoVE and other relevant links can be found on the ORNL DAAC's ABoVE Project Page.
Citation: Zhang, Y., C.E. Woodcock, S. Chen, J. Wang, D. Sulla-Menashe, Z. Zuo, P. Olofsson, Y. Wang, and M.A. Friedl. 2022. ABoVE: Landsat-derived Annual Disturbance Agents Across ABoVE Core Domain, 1987-2012. ORNL DAAC, Oak Ridge, Tennessee, USA. https://doi.org/10.3334/ORNLDAAC/1924