The ORNL DAAC recently released a new Arctic-Boreal Vulnerability Experiment (ABoVE) dataset by Huemmrich, K.F., et al. (2022):
Tundra Plant Leaf-level Spectral Reflectance and Chlorophyll Fluorescence, 2019-2021
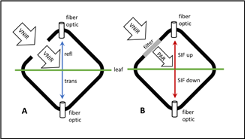
This dataset provides leaf-level visible-near infrared spectral reflectance, chlorophyll fluorescence spectra, species, plant functional type (PFT), and chlorophyll content of common high latitude plant samples collected near Fairbanks, Utqiagvik, and Toolik, Alaska, U.S., during the summers of 2019, 2020, and 2021. A FluoWat leaf clip was used to measure leaf-level visible-near infrared spectral reflectance and chlorophyll fluorescence spectra. Fluorescence yield (Fyield) was calculated as the ratio of the emitted fluorescence divided by the absorbed radiation for the wavelengths from 400 nm up to the wavelength of the cut off for the FluoWat low pass filter (either 650 or 700 nm). Chlorophyll content of samples was measured using a CCM-300 Chlorophyll Content. The data are provided in comma-separated values (.csv) format.
The ABoVE is a NASA Terrestrial Ecology Program field campaign being conducted in Alaska and western Canada, for 8 to 10 years, starting in 2015. Research for ABoVE links field-based, process-level studies with geospatial data products derived from airborne and satellite sensors, providing a foundation for improving the analysis, and modeling capabilities needed to understand and predict ecosystem responses to, and societal implications of, climate change in the Arctic and Boreal regions.
Additional data from ABoVE and other relevant links can be found on the ORNL DAAC's ABoVE Project Page.
Citation: Huemmrich, K.F., and P.K. Campbell. 2022. Tundra Plant Leaf-level Spectral Reflectance and Chlorophyll Fluorescence, 2019-2021. ORNL DAAC, Oak Ridge, Tennessee, USA. https://doi.org/10.3334/ORNLDAAC/2005