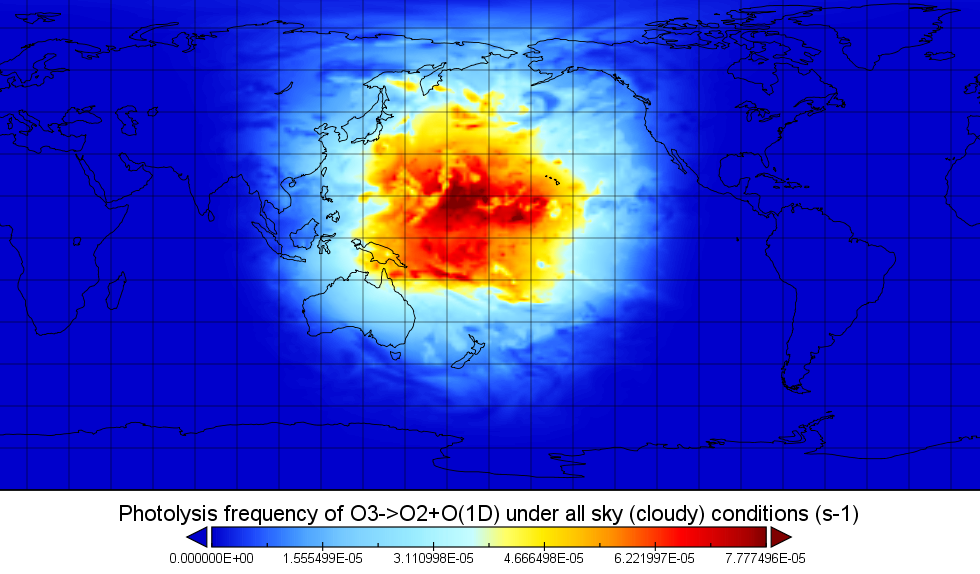
ATom: Global Modeled and CAFS Measured Cloudy and Clear Sky Photolysis Rates, 2016
This dataset from the Atmospheric Tomography Mission (ATom) provides the results from nine global chemistry-climate or chemistry-transport models that estimated gridded values of atmospheric photolytic rates (J values) for ozone (O3) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2) under cloudy and clear sky scenarios. Each model produced global 4-D fields (latitude by longitude by pressure for 24 hours) for one day in mid-August 2016 (nominally) of results from two simulations: first using their standard treatment of clouds (all sky or cloudy) and a second with clouds and aerosols removed (clear sky). Atmospheric photolytic rates were collected with the Charged-coupled device Actinic Flux Spectroradiometer (CAFS) instrument. CAFS measurements provide an extensive set of statistics on how clouds alter photolysis rates and provide a unique opportunity to test how the chemistry models treat clouds in comparison to the in-situ measurements throughout the remote Pacific and Atlantic Ocean basins.
ATom is a NASA Earth Venture Suborbital-2 mission that will study the impact of human-produced air pollution on greenhouse gases and on chemically reactive gases in the atmosphere. ATom deploys an extensive gas and aerosol payload on the NASA DC-8 aircraft for systematic, global-scale sampling of the atmosphere, profiling continuously from 0.2 to 12 km altitude. Flights will occur in each of 4 seasons over a 4-year period. See all data from ATom.
Data Citation: Hall, S.R., K. Ullmann, M.J. Prather, C.M. Flynn, L.T. Murray, A.M. Fiore, G. Correa, S.A. Strode, S.D. Steenrod, J.-F. Lamarque, J. Guth, B. Josse, J. Flemming, V. Huijnen, N.L. Abraham, and A.T. Archibald. 2019. ATom: Global Modeled and CAFS Measured Cloudy and Clear Sky Photolysis Rates, 2016. ORNL DAAC, Oak Ridge, Tennessee, USA. https://doi.org/10.3334/ORNLDAAC/1651
Data Center: ORNL DAAC
Sponsor: EOSDIS