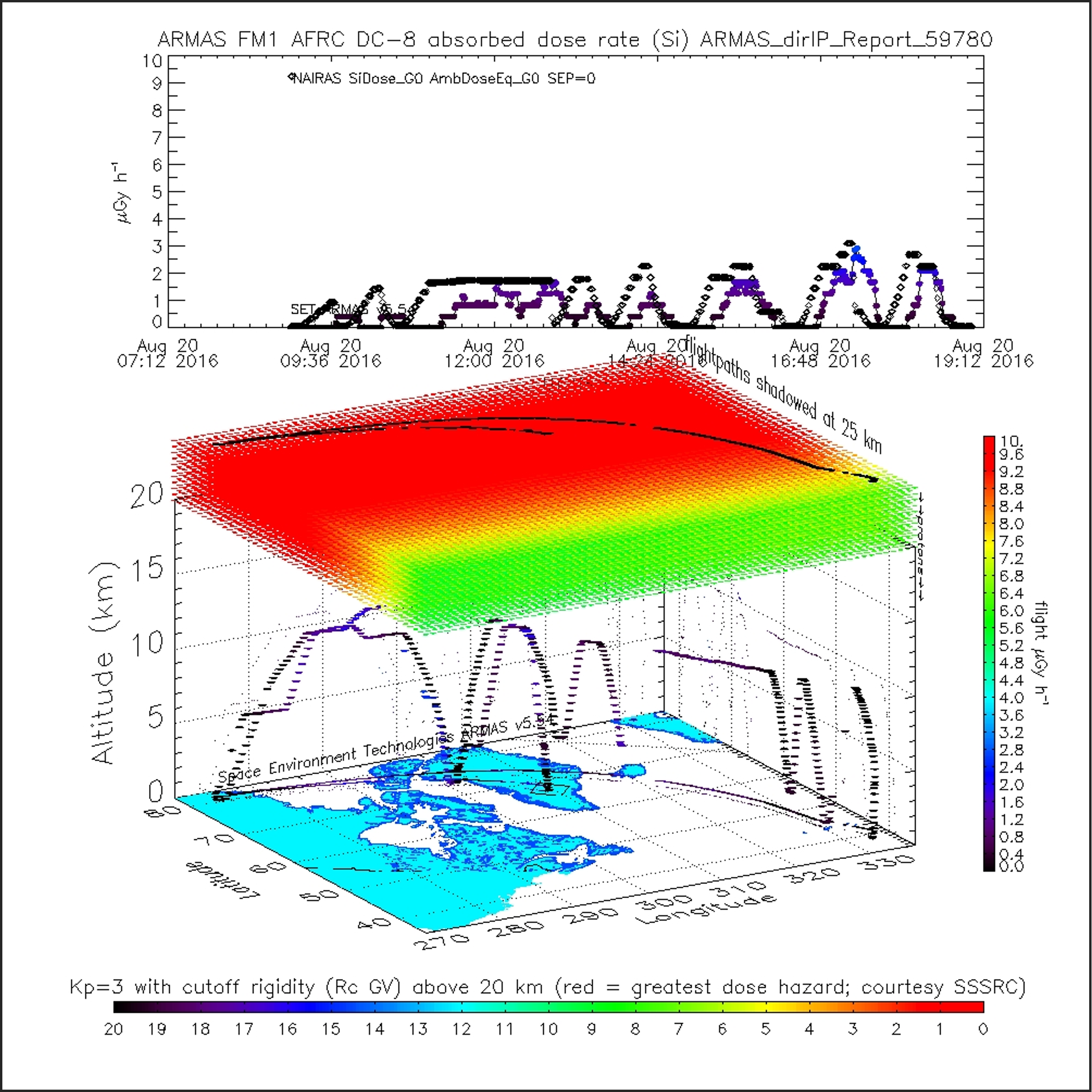
The ORNL DAAC recently released the following Atmospheric Tomography Mission (ATom) dataset by Tobiska, W.K. (2021):
ATom: ARMAS Program Absorbed and Equivalent Radiation Dose Rates for ATom-1 Campaign
This dataset contains absorbed radiation dose rates in silicon from the Automated Radiation Measurements for Aerospace Safety (ARMAS) system along ATom flight paths for the ATom-1 campaign conducted in July and August 2016. Absorbed dose rates measure how much energy is deposited in matter by ionizing radiation per unit time. Radiation sources can be from galactic cosmic rays, solar energetic particles, or Van Allen radiation belt energetic particles and can have adverse effects on human tissue and aerospace electronics as well as profound effects on chemical species in the atmosphere. Derived ambient equivalent dose rates are provided and relate the absorbed dose in human tissue to the effective biological damage of the radiation through a radiation weighting factor. Visualizations of absorbed radiation dose for ATom-1 flight paths are included.
The Atmospheric Tomography Mission (ATom) is a NASA Earth Venture Suborbital-2 mission to study the impact of human-produced air pollution on greenhouse gases and on chemically reactive gases in the atmosphere. ATom deployed an extensive gas and aerosol payload on the NASA DC-8 aircraft for systematic, global-scale sampling of the atmosphere, profiling continuously from 0.2 to 12 km altitude. Around-the-world flights were conducted in each of four seasons between 2016 and 2018.
Additional data from ATom and other relevant links can be found on the ORNL DAAC's ATom Project Page.
Citation: Tobiska, W.K. 2021. ATom: ARMAS Program Absorbed and Equivalent Radiation Dose Rates for ATom-1 Campaign. ORNL DAAC, Oak Ridge, Tennessee, USA. https://doi.org/10.3334/ORNLDAAC/1906