“With AfriSAR, we’re getting very accurate measurements of the 3-D structure of an ecosystem that is representative of the larger Congo Basin rainforest and of tropical forests in general, and this is going to allow us to get a better grip on how much carbon is stored in these ecosystems.” – Lola Fatoyinbo, NASA lead for AfriSAR
The 2016 AfriSAR campaign collected radar, LiDAR, and field measurements of tropical forests in Gabon, West Africa. The campaign was part of an ongoing NASA collaboration with the European Space Agency (ESA) and the Gabonese Space Agency. The AfriSAR data is a precursor to upcoming spaceborne missions, including GEDI, that examine the role of forests in Earth's carbon cycle.
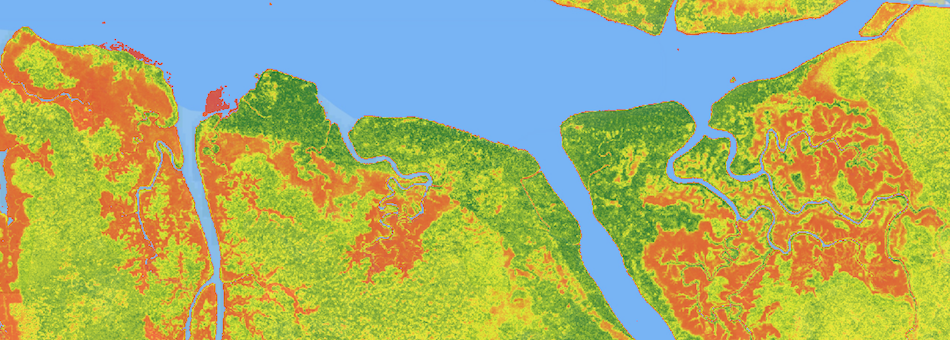
During February and March 2016, NASA‘s Uninhabited Aerial Vehicle Synthetic Aperture Radar (UAVSAR) and Land, Vegetation, and Ice Sensor (LVIS) instruments collected data used to derive forest canopy height, 3-D forest structure, and topography. Ground-based field measurements were also collected to calibrate the airborne data. These data will be used to estimate the amount of carbon stored in Gabon’s forests.
AfriSAR data now available:
AfriSAR: Rainforest Canopy Height Derived from PolInSAR and Lidar Data, Gabon
AfriSAR: Canopy Structure Derived from PolInSAR and Coherence TomoSAR NISAR tools
AfriSAR: Canopy Cover and Vertical Profile Metrics Derived from LVIS, Gabon, 2016
AfriSAR: Mondah Forest Tree Species, Biophysical, and Biomass Data, Gabon, 2016
Read more on NASA's Earth Observatory Blog and The Armstrong X-Press .