The ORNL DAAC recently released a new dataset from the Carbon Monitoring System (CMS) project by Lu, X., et al., (2023):
Fire Particulate Emissions from Combined VIIRS and AHI Data for Indonesia, 2015-2020
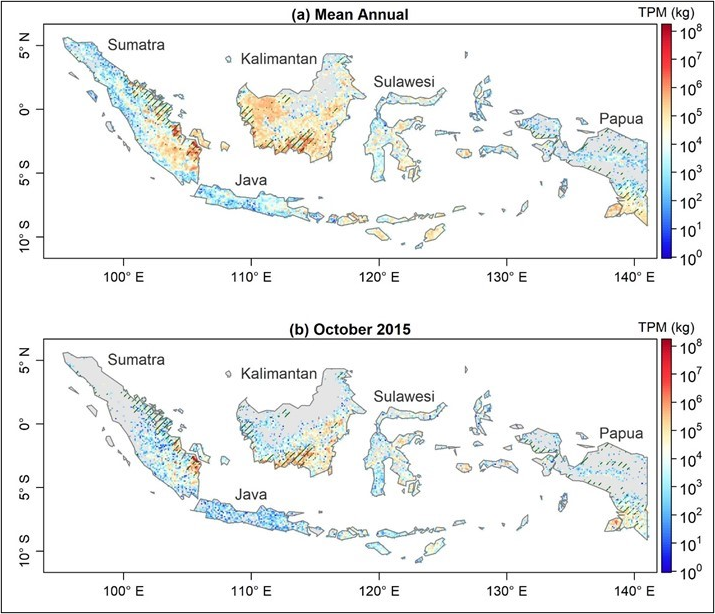
This dataset provides 10-minute fire emissions within 0.1-degree regularly spaced intervals across Indonesia from July 2015 to December 2020. The dataset was produced with a top-down approach based on fire radiative energy (FRE) and smoke aerosol emission coefficients (Ce) derived from multiple new-generation satellite observations. Specifically, the Ce values of peatland, tropical forest, cropland, or savanna and grassland were derived from fire radiative power (FRP) and emission rates of smoke aerosols based on Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) active fire and aerosol products. FRE for each 0.1-degree interval was calculated from the diurnal FRP cycle that was reconstructed by fusing cloud-corrected FRP retrievals from the high temporal-resolution (10 mins) Himawari-8 Advanced Himawari Imager (AHI) with those from high spatial-resolution (375 m) VIIRS. This new dataset was named the Fused AHI-VIIRS based fire Emissions (FAVE). Fire emissions data are provided in comma-separated values (CSV) format with one file per month from July 2015 to December 2020. Each file includes variables of fire observation time, fire geographic location, classification, fire radiative energy, various fire emissions and related standard deviations.
The NASA CMS program is designed to make significant contributions in characterizing, quantifying, understanding, and predicting the evolution of global carbon sources and sinks through improved monitoring of carbon stocks and fluxes. The System uses NASA satellite observations and modeling/analysis capabilities to establish the accuracy, quantitative uncertainties, and utility of products for supporting national and international policy, regulatory, and management activities. CMS data products are designed to inform near-term policy development and planning.
Additional data from Carbon Monitoring System (CMS) project and other relevant links can be found on the ORNL DAAC's CMS Project Page.
Citation: Lu, X., X. Zhang, F. Li, and M.A. Cochrane. 2023. Fire Particulate Emissions from Combined VIIRS and AHI Data for Indonesia, 2015-2020. ORNL DAAC, Oak Ridge, Tennessee, USA. https://doi.org/10.3334/ORNLDAAC/2118