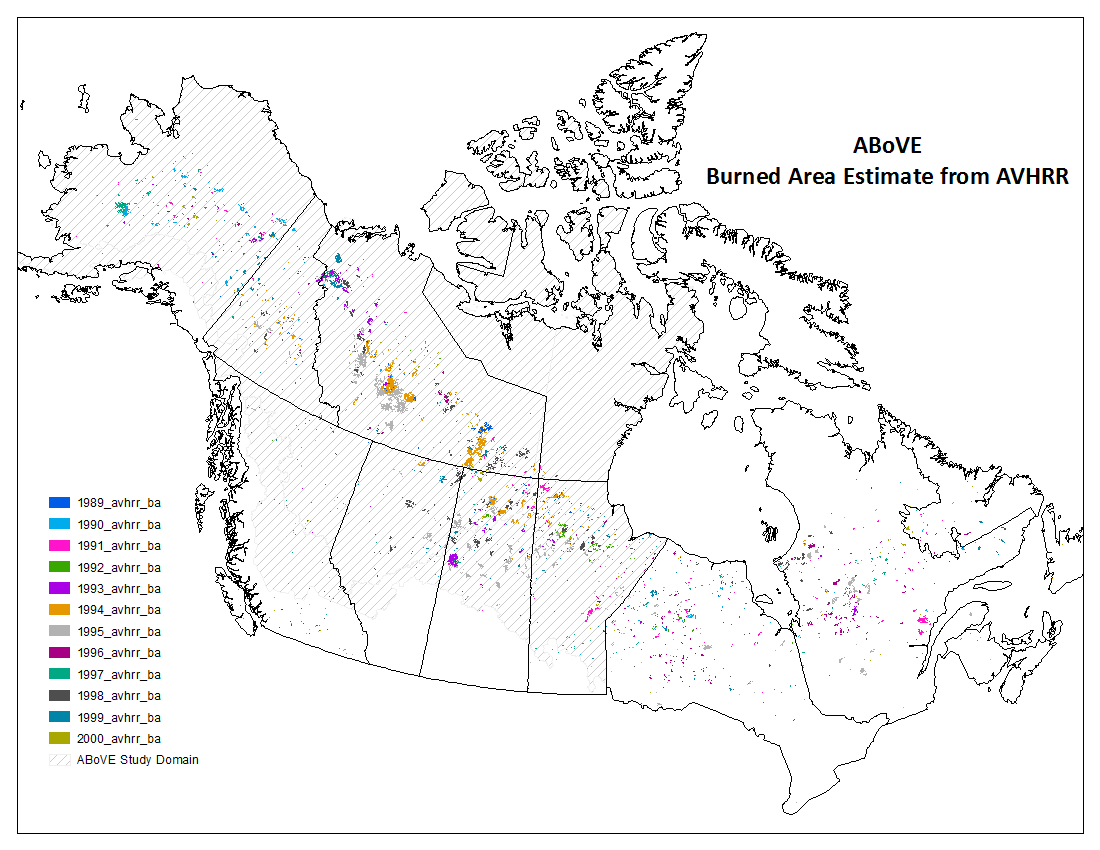
Advanced very-high-resolution radiometer (AVHRR) instruments are used for remotely determining cloud cover and surface temperature. AVHRR data can also be useful in studying climate change and environmental changes, such as forest fire burned areas and hot spots.
A new dataset archived at the ORNL DAAC provides annual forest fire burned area and daily hotspot products developed using data acquired from AVHRR instruments carried aboard two NOAA polar-orbiting satellites (NOAA-11 and NOAA-14). The fire products were generated over 12 fire seasons (1st May - 31st October) from 1989-2000 across North America at 1-km resolution and subset to the ABoVE spatial domain of Alaska and Canada.
Data access: ABoVE: AVHRR-Derived Forest Fire Burned Area-Hot Spots, Alaska and Canada, 1989-2000
Data Citation:
Pu, R., Z. Li, P. Gong, I.A. Csiszar, R. Fraser, W.M. Hao, and S. Kondragunta. 2018. ABoVE: AVHRR-Derived Forest Fire Burned Area-Hot Spots, Alaska and Canada, 1989-2000. ORNL DAAC, Oak Ridge, Tennessee, USA. https://doi.org/10.3334/ORNLDAAC/1545
Data center: ORNL DAAC
Sponsor: NASA EOSDIS