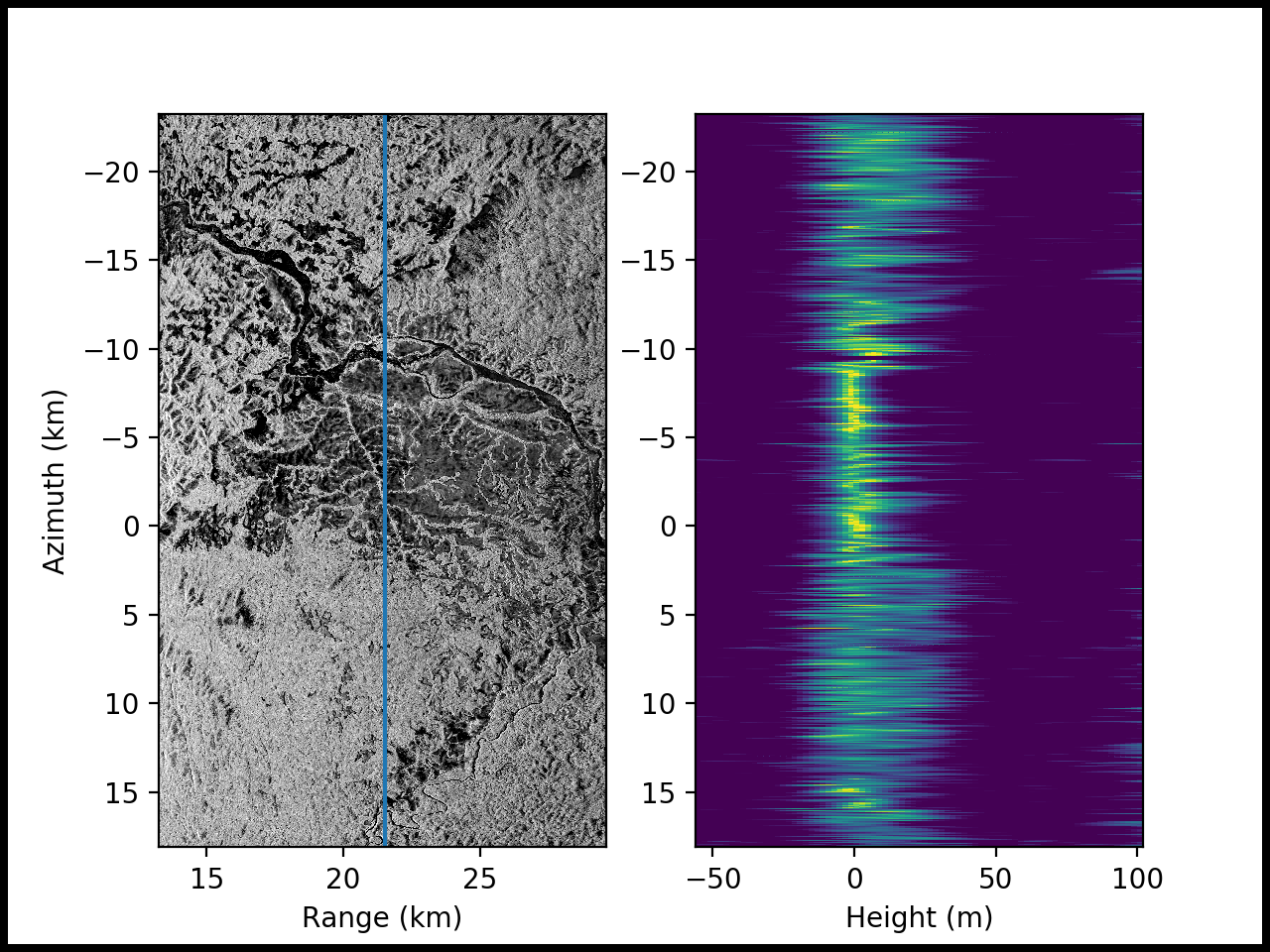
AfriSAR: Polarimetric Height Profiles by TomoSAR, Lope and Rabi Forests, Gabon, 2016
This dataset provides height profiles derived from UAVSAR (Uninhabited Aerial Vehicle Synthetic Aperture Radar; JPL) data acquired over Lope National Park and Rabi Forest in Gabon as part of the AfriSAR campaign in 2016. These data were produced using synthetic aperture radar tomography (TomoSAR), a method that reveals three-dimensional forest structures by extending the conventional two-dimensional imaging capabilities of radars using multiple images acquired from slightly different antenna positions. SAR tomography is an extension of conventional SAR imaging techniques in which a scene is acquired multiple times from slightly different vantage points, then combines images to determine the radar backscatter at arbitrary points within a 3D volume of space.
The AfriSAR mission was an airborne campaign that collected radar and field measurements of forests in Gabon, West Africa. The mission was a NASA collaboration with the European Space Agency (ESA) and the Gabonese Space Agency. The AfriSAR data will help prepare for and calibrate current and upcoming spaceborne missions that aim to gauge the role of forests in Earth's carbon cycle.
See all data from AfriSAR.
Data Citation: Hawkins, B.P., N. Pinto, M. Lavalle, and S. Hensley. 2018. AfriSAR: Polarimetric Height Profiles by TomoSAR, Lope and Rabi Forests, Gabon, 2016. ORNL DAAC, Oak Ridge, Tennessee, USA. https://doi.org/10.3334/ORNLDAAC/1577
Data Center: ORNL DAAC
Sponsor: EOSDIS