The ORNL DAAC recently released a new Arctic-Boreal Vulnerability Experiment (ABoVE) dataset by Macander, M., et al. (2021):
ABoVE: Lichen Forage Cover over Fortymile Caribou Range, Alaska and Yukon, 2000-2015
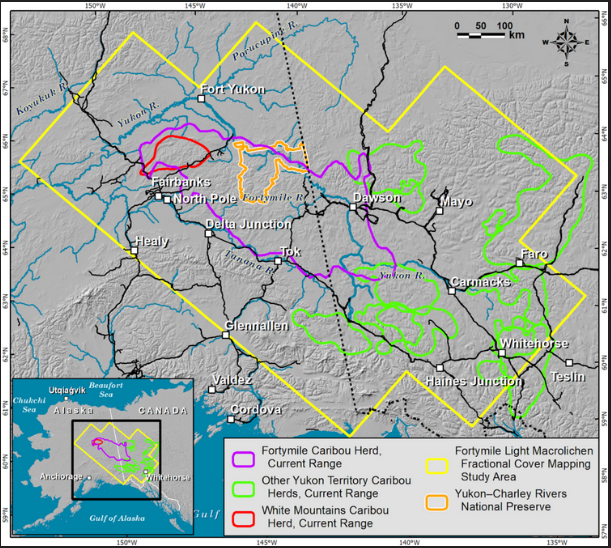
This dataset provides modeled estimates of lichen ground cover at 30 m resolution across the Fortymile study area in interior eastern Alaska, U.S., and the Yukon Territory, Canada, for the nominal year 2015. A random forest modeling approach with vegetation inputs and environmental and spectral predictors was used to estimate lichen cover for 2015. Input data for the model were aggregated from historical in-situ vegetation plots, visual aerial surveys, and recent unmanned aerial system (UAS) imagery to align with 30 m resolution Landsat pixels over the 583,200 km2 study area. The model was also used to estimate lichen cover for the year 2000 by applying the trained model to historical Landsat imagery. An estimate of lichen volume in 2015, based on a published algorithm, is also provided.
The ABoVE is a NASA Terrestrial Ecology Program field campaign being conducted in Alaska and western Canada, for 8 to 10 years, starting in 2015. Research for ABoVE links field-based, process-level studies with geospatial data products derived from airborne and satellite sensors, providing a foundation for improving the analysis, and modeling capabilities needed to understand and predict ecosystem responses to, and societal implications of, climate change in the Arctic and Boreal regions.
Additional data from ABoVE and other relevant links can be found on the ORNL DAAC's ABoVE Project Page.
Citation: Macander, M., E.C. Palm, G.V. Frost, and P.R. Nelson. 2021. ABoVE: Lichen Forage Cover over Fortymile Caribou Range, Alaska and Yukon, 2000-2015. ORNL DAAC, Oak Ridge, Tennessee, USA. https://doi.org/10.3334/ORNLDAAC/1867