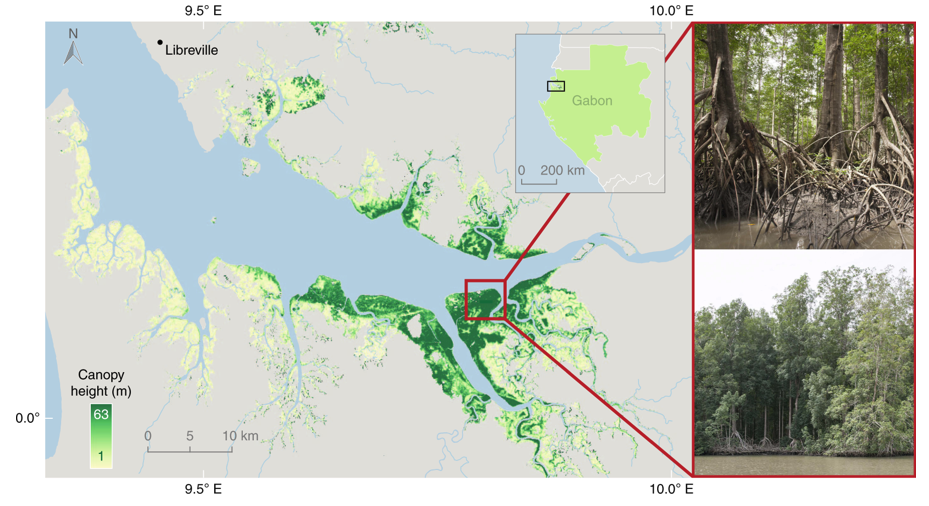
The ORNL DAAC recently released an update to the following Carbon Monitoring System (CMS) datasets by Simard, M., et al. (2019):
Global Mangrove Distribution, Aboveground Biomass, and Canopy Height
In this release, an in-situ tree measurement data file and documentation are included but otherwise no changes were made to previously archived data. This dataset characterizes the global distribution, biomass, and canopy height of mangrove-forested wetlands based on remotely sensed and in-situ field measurement data. Spatially explicit estimates of mangrove canopy height and AGB derived from space-borne remote sensing data and in-situ measurements were used to assess local-scale geophysical and environmental conditions that regulate forest structure and carbon cycle dynamics. These data revealed a wide range of canopy heights, including maximum values (> 62 m) that surpass maximum heights of other forest types.
The NASA CMS program is designed to make significant contributions in characterizing, quantifying, understanding, and predicting the evolution of global carbon sources and sinks through improved monitoring of carbon stocks and fluxes. The System uses NASA satellite observations and modeling/analysis capabilities to establish the accuracy, quantitative uncertainties, and utility of products for supporting national and international policy, regulatory, and management activities. CMS data products are designed to inform near-term policy development and planning.
Additional data from CMS and other relevant links can be found on the ORNL DAAC's CMS Project Page.
Citation: Simard, M., T. Fatoyinbo, C. Smetanka, V.H. Rivera-monroy, E. Castaneda, N. Thomas, and T. Van der stocken. 2019. Global Mangrove Distribution, Aboveground Biomass, and Canopy Height. ORNL DAAC, Oak Ridge, Tennessee, USA. https://doi.org/10.3334/ORNLDAAC/1665