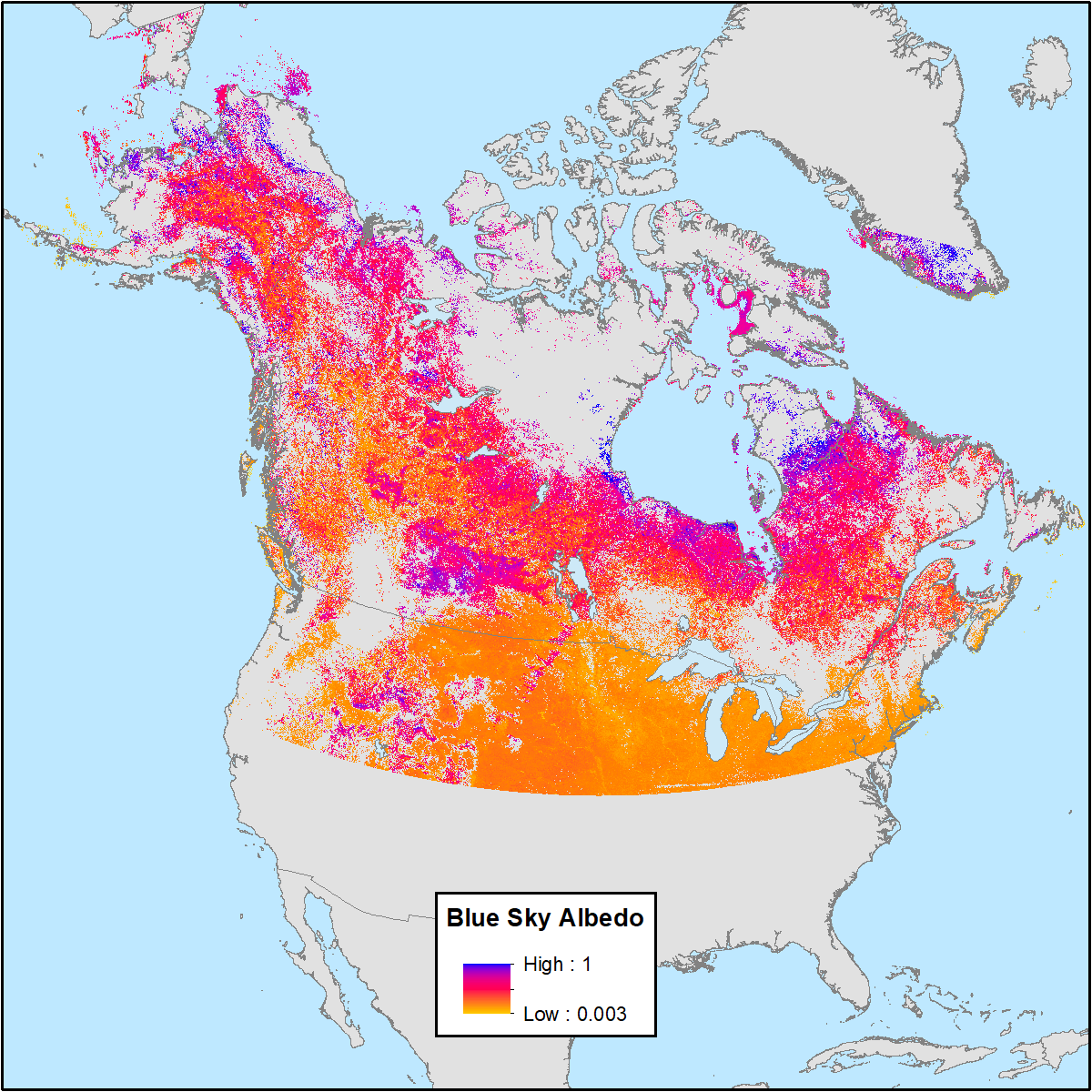
ABoVE: MODIS-Derived Daily Mean Blue Sky Albedo for Northern North America, 2000-2017
This dataset from the Arctic-Boreal Vulnerability Experiment (ABoVE) contains MODIS-derived daily mean shortwave blue sky albedo for North America above 40 degrees North and a set of quality control flags for each albedo value to aid in user interpretation. The data cover the period of available MODIS data, February 24, 2000 through April 22, 2017 (6,264 days). The blue sky albedo data were derived from the MODIS 500-m bi-directional reflectance distribution function (BRDF) product (MCD43 V006). Blue sky refers to albedo calculated under real-world conditions with a combination of both diffuse and direct lighting based on atmospheric and view-geometry conditions.
ABoVE is a NASA Terrestrial Ecology Program field campaign conducted in Alaska and western Canada between 2016 and 2021. Research for ABoVE links field-based, process-level studies with geospatial data products derived from airborne and satellite sensors, providing a foundation for improving the analysis, and modeling capabilities needed to understand and predict ecosystem responses to, and societal implications of, climate change in the Arctic and Boreal regions. See all ORNL DAAC data from ABoVE.
Data Citation: Solvik, K., S. Potter, A.M. Erb, M. Roman, C. Schaaf, Q. Sun, Z. Wang, and B.M. Rogers. 2019. ABoVE: MODIS-Derived Daily Mean Blue Sky Albedo for Northern North America, 2000-2017. ORNL DAAC, Oak Ridge, Tennessee, USA. https://doi.org/10.3334/ORNLDAAC/1605
Data Center: ORNL DAAC
Sponsor: EOSDIS