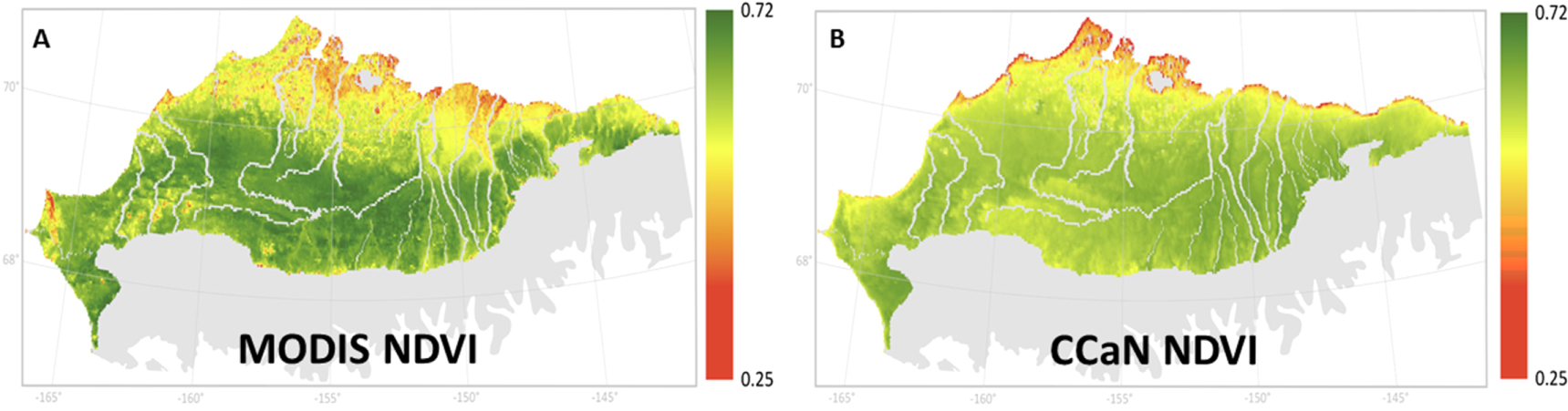
ABoVE: MODIS- and CCAN-Derived NDVI and Trends, North Slope of Alaska, 2000-2015
The Arctic-Boreal Vulnerability Experiment (ABoVE) provides a new dataset of the average Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) at 1 km resolution over the north slope of Alaska, USA, for the growing season (June-August) of each year from 2000-2015, and NDVI trends for the same period. This dataset presents growing-season averages and trends from two sources: 1) derived from 1 km, 8 day data from the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) NDVI (MOD13A2) product, and 2) predicted by the Coupled Carbon and Nitrogen model (CCaN). CCaN is a mass balance carbon and nitrogen model that was driven by 1 km MODIS surface temperature and climate data and parameterized using model-data fusion, where model predictions were ecologically constrained with historical ecological ground and satellite-based data.
Research for ABoVE will link field-based, process-level studies with geospatial data products derived from airborne and satellite sensors, providing a foundation for improving the analysis, and modeling capabilities needed to understand and predict ecosystem responses and societal implications. See all ORNL DAAC datasets from ABoVE
Data Citation: Rocha, A.V., and K.S. Wright. 2019. ABoVE: MODIS- and CCAN-Derived NDVI and Trends, North Slope of Alaska, 2000-2015. ORNL DAAC, Oak Ridge, Tennessee, USA. https://doi.org/10.3334/ORNLDAAC/1666
Data Center: ORNL DAAC
Sponsor: EOSDIS