AfriSAR: Gridded Forest Biomass and Canopy Metrics Derived from LVIS, Gabon, 2016
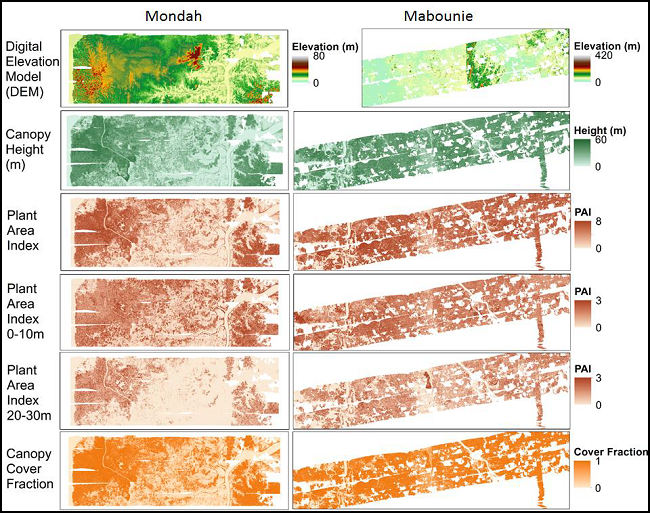
This dataset from AfriSAR contains gridded forest characterization products derived from full-waveform lidar data acquired by NASA's airborne Land, Vegetation, and Ice Sensor (LVIS) instrument for five forested sites in Gabon, Africa, during the 2016 NASA-ESA AfriSAR campaign. The LVIS lidar instrument was flown over study sites in Lope, Mondah/Akanda, Pongara, Rabi, and Mabouni from February to March 2016. Derived canopy cover, canopy heights, bare ground elevation, plant area index (PAI), and foliage height diversity (FHD), and respective uncertainties are provided at a 25 m resolution for each of the five study sites. Aboveground biomass density (AGBD) and uncertainty were modeled at 50 m and 100 m resolutions for the Lope, Mondah, and Mabounie sites using field inventory data and waveform height and cover metrics. Lidar grid cell data collection statistics (i.e., number of shots and flight lines) and a data mask are also included. This research leverages high-quality forest inventory datasets collected during the AfriSAR campaign for one of the least studied and most unique forest ecosystems in the world.
The AfriSAR mission was an airborne campaign that collected radar and field measurements of tropical forests in Gabon, West Africa. The mission was a NASA collaboration with the European Space Agency (ESA) and the Gabonese Space Agency. During the 2016 AfriSAR campaign, NASA UAVSAR and LVIS instruments collected data that will be used to derive forest canopy height, structure, and topography. The AfriSAR data is a precursor to upcoming spaceborne missions that examine the role of forests in Earth's carbon cycle.
Data Citation: Armston, J., H. Tang, S. Hancock, S. Marselis, L. Duncanson, J. Kellner, M. Hofton, J.B. Blair, T. Fatoyinbo, and R.O. Dubayah. 2020. AfriSAR: Gridded Forest Biomass and Canopy Metrics Derived from LVIS, Gabon, 2016. ORNL DAAC, Oak Ridge, Tennessee, USA. https://doi.org/10.3334/ORNLDAAC/1775