Timeseries of Arctic-Boreal Lake Area Derived from CubeSat Imagery, 2017
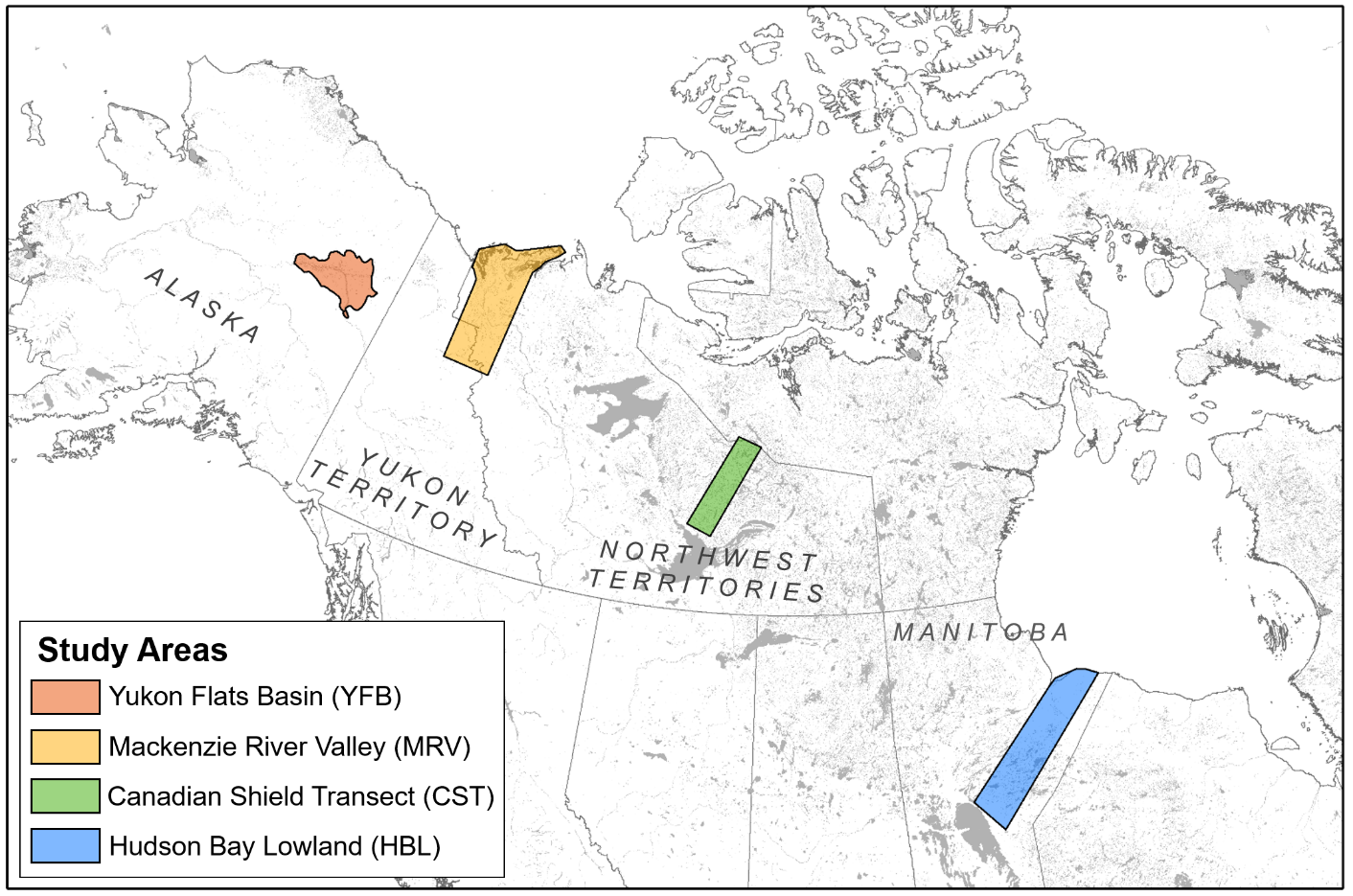
Fluctuations in water level within Arctic-Boreal lakes reflect seasonal hydrological dynamics and may regulate freshwater methane and CO2 emissions. This NASA Arctic-Boreal Vulnerability Experiment (ABoVE) dataset provides near-daily lake area timeseries for 85,358 lakes across four study areas in Northern Canada and Alaska, USA, between May 1 and October 1, 2017. Lake area estimates were produced using digital images from newly developed Planet Labs CubeSats - small satellites with a 4-band (blue, green, red, near-infrared) camera payload. From the imagery, each lake's mean, minimum, and maximum areas and seasonal dynamism were derived. The primary data product is a lake area timeseries for all lakes with a maximum area >0.01 km2.
ABoVE is a NASA Terrestrial Ecology Program field campaign that will link field-based, process-level studies with geospatial data products derived from airborne and satellite sensors, providing a foundation for improving the analysis, and modeling capabilities needed to understand and predict ecosystem responses and societal implications. See data from ABoVE at ORNL DAAC.
Data Citation: Cooley, S.W., L.C. Smith, J.C. Ryan, L.H. Pitcher, and T.M. Pavelsky. 2019. Timeseries of Arctic-Boreal Lake Area Derived from CubeSat Imagery, 2017. ORNL DAAC, Oak Ridge, Tennessee, USA. https://doi.org/10.3334/ORNLDAAC/1667
Data Center: ORNL DAAC
Sponsor: EOSDIS