The ORNL DAAC recently released the Arctic-Boreal Vulnerability Experiment (ABoVE) dataset by Wang, J. et al. (2021):
ABoVE: Annual Aboveground Biomass for Boreal Forests of ABoVE Core Domain, 1984-2014
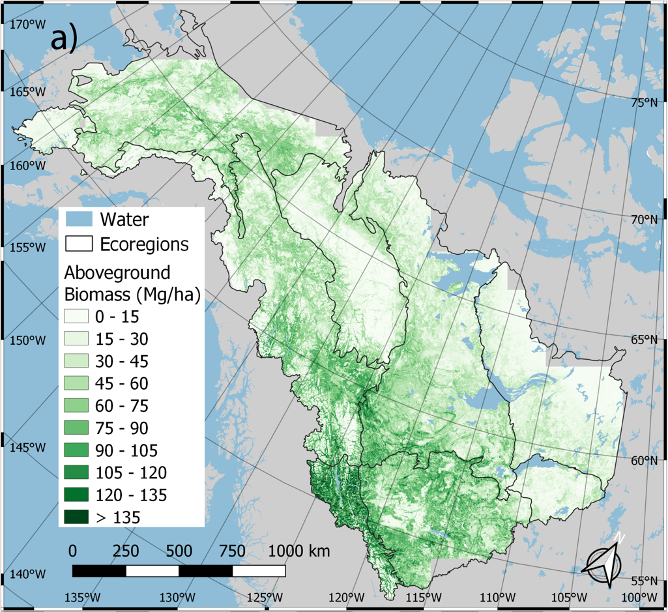
This dataset provides estimated annual aboveground biomass (AGB) density for live woody (tree and shrub) species and corresponding standard errors at a 30 m spatial resolution for the boreal forest biome portion of the Core Study Domain of NASA's Arctic-Boreal Vulnerability Experiment (ABoVE) Project (Alaska and Canada) over the time period 1984-2014. The data were derived from a time series of Landsat-5 and Landsat-7 surface reflectance imagery and full-waveform lidar returns from the Geoscience Laser Altimeter System (GLAS) flown onboard IceSAT from 2004 to 2008. Statistical smoothing at the pixel level was used to reduce noise and uncertainty. These data contribute to the characterization of how biomass stocks are responding to climate and disturbance in boreal forests.
The ABoVE is a NASA Terrestrial Ecology Program field campaign being conducted in Alaska and western Canada, for 8 to 10 years, starting in 2015. Research for ABoVE links field-based, process-level studies with geospatial data products derived from airborne and satellite sensors, providing a foundation for improving the analysis, and modeling capabilities needed to understand and predict ecosystem responses to, and societal implications of, climate change in the Arctic and Boreal regions.
Additional data from ABoVE and other relevant links can be found on the ORNL DAAC's ABoVE Project Page.
Citation: Wang, J., M.K. Farina, A. Baccini, and M.A. Friedl. 2021. ABoVE: Annual Aboveground Biomass for Boreal Forests of ABoVE Core Domain, 1984-2014. ORNL DAAC, Oak Ridge, Tennessee, USA. https://doi.org/10.3334/ORNLDAAC/1808